Dear reader,
I have just undertaken my first trip overseas since the start of the pandemic, flying from London to sunny Spain. It is a good vantage point from which to assess the state of the European travel industry.
While my journey was unaffected by cancelled flights, lost bags or lengthy queues, not every traveller has been so lucky. Customers and shareholders in Scandinavian Airlines (SAS) were at the front of the queue on Tuesday as the airline filed for bankruptcy protection. The restructuring would not have an impact on service levels, the company said. But a pilots’ strike, which was blamed for the urgent need to restructure, could affect up to 30,000 customers.
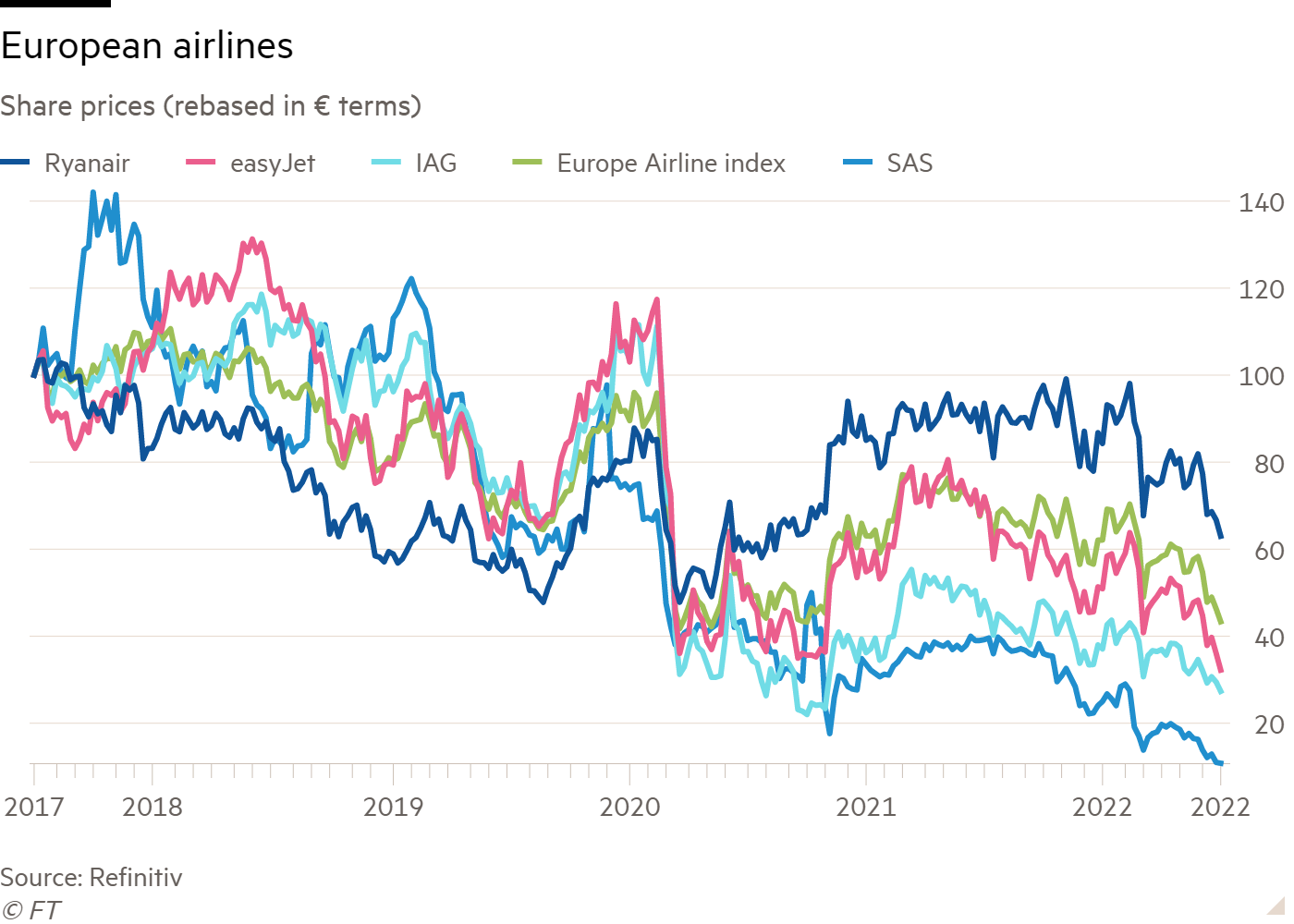
Shares in SAS fell as much as 14 per cent in response. That leaves the company’s equity valued at just under $400mn, down from almost $2bn a year ago.
A sector that was previously hailed as one of the best ways to trade the pandemic recovery is going rapidly downhill.
Customer demand is still high: pandemic-era travel restrictions have eased and travellers are booking holidays. In most countries (excluding China) passenger numbers have either returned to or surpassed 2019 levels. Bookings data suggest the trend will continue into the third quarter of the year.
But for SAS pilots, British Airways’ ground crew and Ryanair’s cabin staff, the problem is pay. Airline staff who accepted cuts during the pandemic to help preserve jobs want to claw back those losses and be compensated for rising living costs.
Along with higher wage bills, airlines are contending with more expensive fuel costs as the price of oil climbs. With interest rates rising, heavily indebted airlines must also consider the prospect of higher debt servicing charges.
As part of its restructuring, SAS hopes to cut $716mn in costs. It will also raise about $900mn in new equity with further plans to swap or pay down almost $2bn of liabilities — about one-third of the total. An existing $741mn of cash on hand will help to smooth the process. The current consensus is that SAS will yield a small operating profit by 2024.
Unlike AirFrance-KLM, which is undergoing its own $2.3bn state-backed rights issue, the Swedish and Danish governments have already ruled out contributing to an SAS rescue plan.
Elsewhere, debt and equity fundraisings over the past two years have kept airline bankruptcies to a minimum. Airlines have largely been able to hold on to the cash that has been raised.
The latest cash balances at IAG, easyJet and Ryanair stood at €8bn, £3.5bn and €3.6bn respectively. If growing fears of a recession in Europe prove true, these will be needed — particularly in the stagflation scenario that many are expecting.
Airlines are only just expected to return to operating profit this year. Stress testing shows that interest cover for IAG and easyJet falls below expected operating earnings if interest costs double and ebit is one quarter less than current expectations.
A less indebted airline such as Ryanair would hold up better, with interest covered five times even in a stagflationary scenario. Along with better fuel hedges and growing market share, there is reason to think Europe’s best-performing airline will be able to hang on to its title.
Fuel costs are already high and interest payments are likely to rise. Staffing overheads remain the only real lever for cost-conscious airlines. That does not bode well for shareholders or air passengers. Wish me luck for my return journey to London.
Andrew Whiffin
Lex writer
If you would like to receive regular updates whenever we publish Lex, do add us to your FT Digest, and you will get an instant email alert every time we publish. You can also see every Lex column via the webpage